클로저와 스코프
🌲 렉시컬 스코프와 동적 스코프 (Lexical Scope vs Dynamic Scope)
렉시컬 스코프
lexical scope, static scope, rhetorical scope라고도 불린다.
name resolution depends on the location in the source code and the lexical context (also called static context), which is defined by where the named variable or function is defined.
렉시컬 스코프는 변수나 함수가 정의된 그 시점에 결정이 된다.
동적 스코프
the name resolution depends upon the program state when the name is encountered which is determined by the execution context (also called runtime context, calling context or dynamic context).
동적 스코프는 실행 컨텍스트에 따라 결정이 된다.
🌲 스코프
자바스크립트는 렉시컬 스코프이다. 렉시컬 스코프는 어떤 변수가 함수 스코프 안에 있는지 함수를 정의할 때 알 수 있다는 것이다. 호출할 때 알 수 있는 것이 아니다.
자바스크립트의 렉시컬 스코프는 global scope, function scope, block scope에 정의된다.
1. 전역 스코프 - Global Scope
전역 스코프에서 선언한 것은 무엇이든 프로그램의 모든 스코프에서 볼 수 있다. 전역 스코프에서 선언된 것들을 전역변수라고 한다. 전역변수에 의존하는 것은 피해야 한다.
2. 함수 레벨 스코프 - Function Scope
var로 선언된 변수나, 함수 선언식으로 만들어진 함수는 함수 레벨 스코프를 갖는다. 이는 함수 내부에 선언된 식별자는 함수 내부에서만 유효하다는 것이다.
위의 코드에서 hello는 함수 레벨 스코프이기 때문에 console.log는 hello 변수를 참조할 수 있다. 만약 hello가 var가 아닌 const나 let으로 선언되었다면, 블록 스코프의 영향을 받기 때문에, console.log에서는 hello를 참조할 수 없었을 것이다.
3. 블록 스코프 - Block Scope
ES6부터 블록 레벨 스코프를 지원하기 시작하였다. 블록이란 중괄호{}로 묶은 것이다. let 과 const 는 블록 스코프 변수를 만들어준다. 모든 코드 블록 내에서 선언된 변수는 코드 블록 내에서만 유효하다.
🌲 스코프 체인
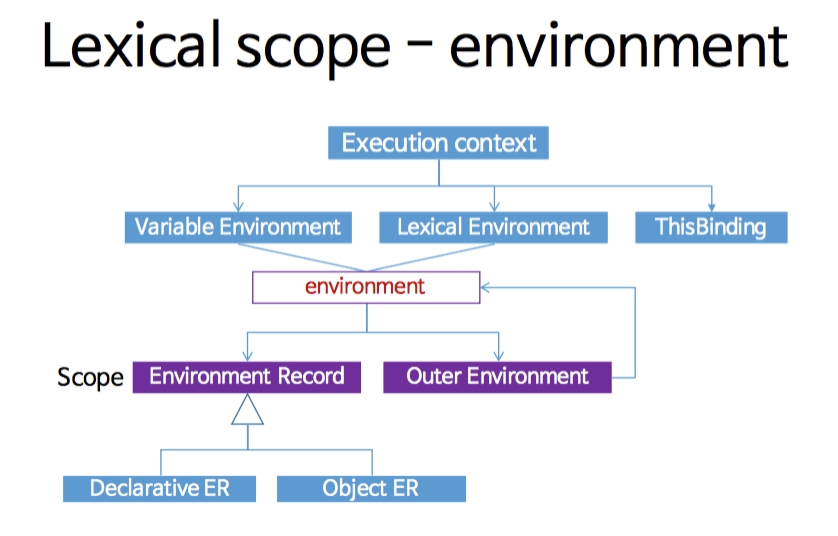
렉시컬 환경은 Environment Record와 Outer Environment에 대한 참조로 이루어져 있다. 변수를 찾을 때 Environment Record에서 먼저 찾아보고, 없으면 Outer Environment의 환경 레코드에서 찾아본다. 변수를 찾을 때까지 바깥 환경을 찾다가, global scope에도 존재하지 않을 때까지 찾게 된다. global scope에도 존재하지 않으면, Reference Error가 발생하게 된다. 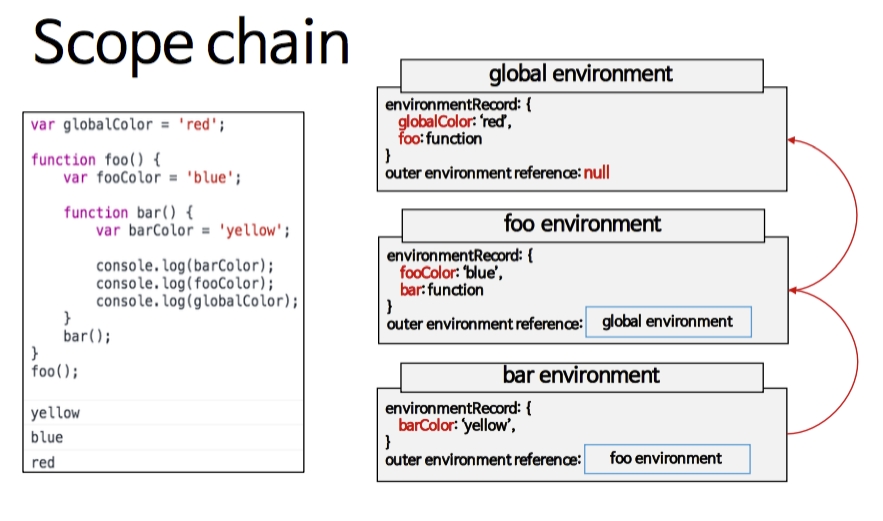
🌲 클로져 - Closure
클로저는 현재의 유효 범위를 넘어서, 스코프 체인으로 연결된 변수 객체에서 변수에 대한 참조를 하는 것을 말한다.
javascript의 스코프는 함수가 생성될 때의 [[Scope]] 프로퍼티로 참조하고 있는 변수 객체들과, 함수가 실행될 때의 변수 객체를 참조하고 있다. 따라서, 현재의 scope에 없는 변수 또한, scope chain을 통해 참조가 가능하다.
클로저 예제
baz는 global에서 실행되었지만, color로 blue를 참조하였다. 이는 bar 함수의 렉시컬 환경이 outer environment로 foo environment를 참조하고 있었기 때문이다. 자바스크립트는 렉시컬 스코프이기 때문에 실행 컨텍스트와 관계 없이, bar environment는 foo environment를 outer lexical environment로 결정하게 된다. 따라서 global에서 baz를 호출하더라도 outer environment인 foo에서 color를 찾은 것이다. 이러한 bar와 같은 함수를 클로저라고 한다.
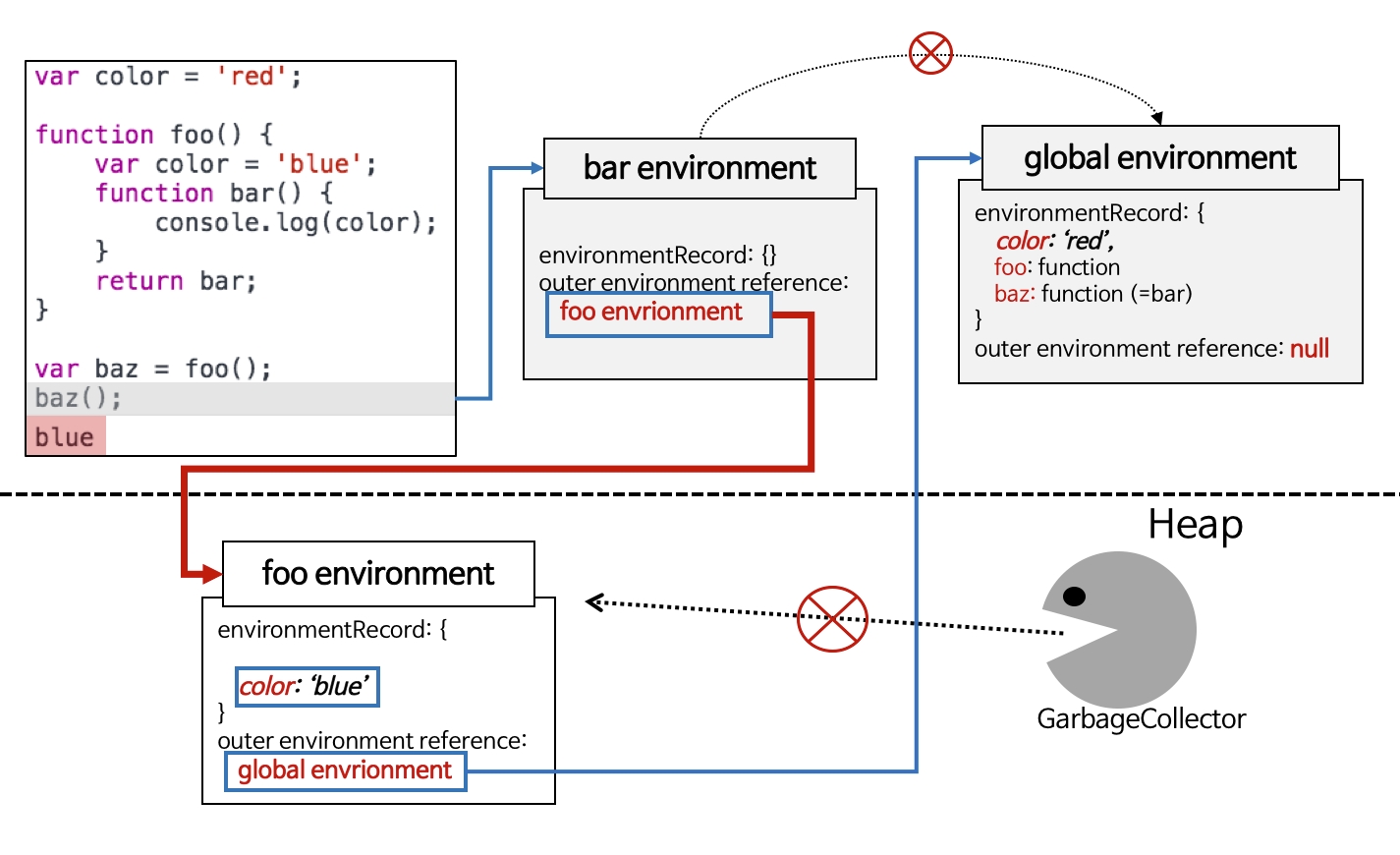
추가로 foo environment는 foo() 수행이 끝난 후 가비지 컬렉터가 회수해야 하지만, 실제로는 그렇지 않다. bar environment가 foo의 렉시컬 환경을 참조하고 있고, bar는 baz가 참조하고 있기 때문에, GC가 회수하지 않게 된다.
참조
Last updated