함수 호출 방식과 this 바인딩
자바스크립트는 함수 호출 방식에 의해 this에 바인딩되는 객체가 동적으로 결정된다.
즉, 함수를 호출할 때 함수가 어떻게 호출되었는지에 따라 this가 동적으로 결정된다.
함수 호출 방식은 다음과 같다.
함수 호출
메서드 호출
생성자 함수 호출
apply / call / bind 호출
const foo = function () {
console.dir(this);
};
// 1. 함수 호출
foo();
// 2. 메서드 호출
const obj = { foo: foo };
obj.foo();
// 3. 생성자 함수 호출
const instance = new foo();
// 4. apply, call, bind 호출
const bar = { name: "bar" };
foo.call(bar);
foo.apply(bar);
foo.bind(bar);🌳 1. 함수 호출
전역 객체(GO) 는 모든 객체의 유일한 최상위 객체이다.
브라우저에서는 window, 서버에서는 global 객체를 가리킨다.
전역 객체는 전역 스코프를 갖는 전역 변수를 프로퍼티로 갖고 있다. 글로벌 영역에서 선언한 함수는 전역객체의 프로퍼티로 접근할 수 있는 전역 변수 메서드이다.
const나 let 키워드로 선언된 전역 변수는 전역 객체의 프로퍼티가 아니다.
기본적으로 this는 전역객체에 바인딩된다.
내부함수의 경우에도 전역 객체에 바인딩된다.
메서드의 내부함수 일 경우에도 전역 객체에 바인딩 된다.
콜백 함수 일 때에도, this는 전역 객체에 바인딩 된다.
화살표함수의 경우에는 this가 정적으로 결정되는데, 이 때 this는 상위 스코프의 this를 가리킨다.
명시적으로 this를 결정하는 방식은,
apply,call,bind메서드를 사용하는 것이다.
🌳 2. 메서드 호출
함수가 객체의 프로퍼티일 때, 함수를 메서드라고 한다.
메서드 내부의 this는 해당 메서드를 호출한 객체에 바인딩 된다.
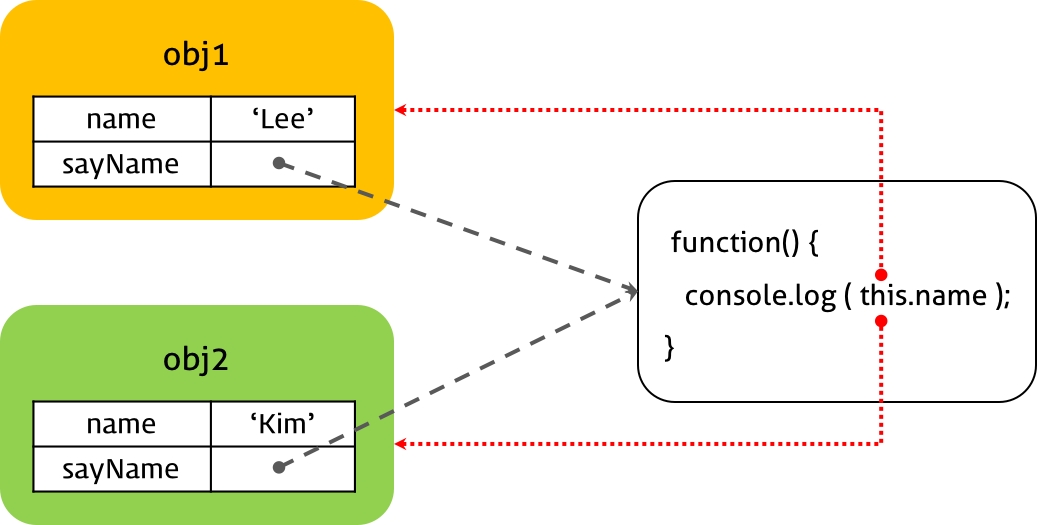
프로토타입의 메서드의 경우에도, 해당 메서드를 호출한 객체에 바인딩된다.
🌳 3. 생성자 함수 호출
생성자 함수란?
객체를 생성하는 역할
형식이 정해져있지 않으며, 기존 함수에
new연산자를 붙여서 호출하면, 해당 함수는 생성자 함수로 동작한다.일반적으로 생성자 함수명은 첫 문자를 대문자로 표기하여, 생성자 함수임을 나타낸다.
생성자 함수 동작 방식
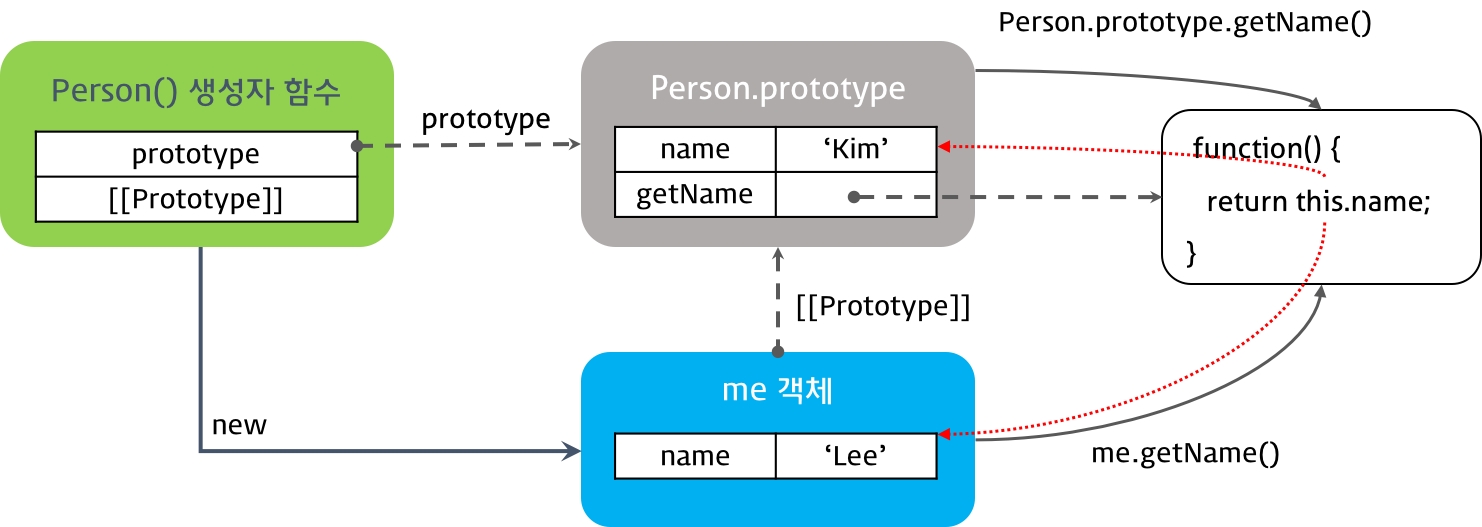
new 연산자로 생성자 함수 호출 시 다음과 같은 순서로 동작한다.
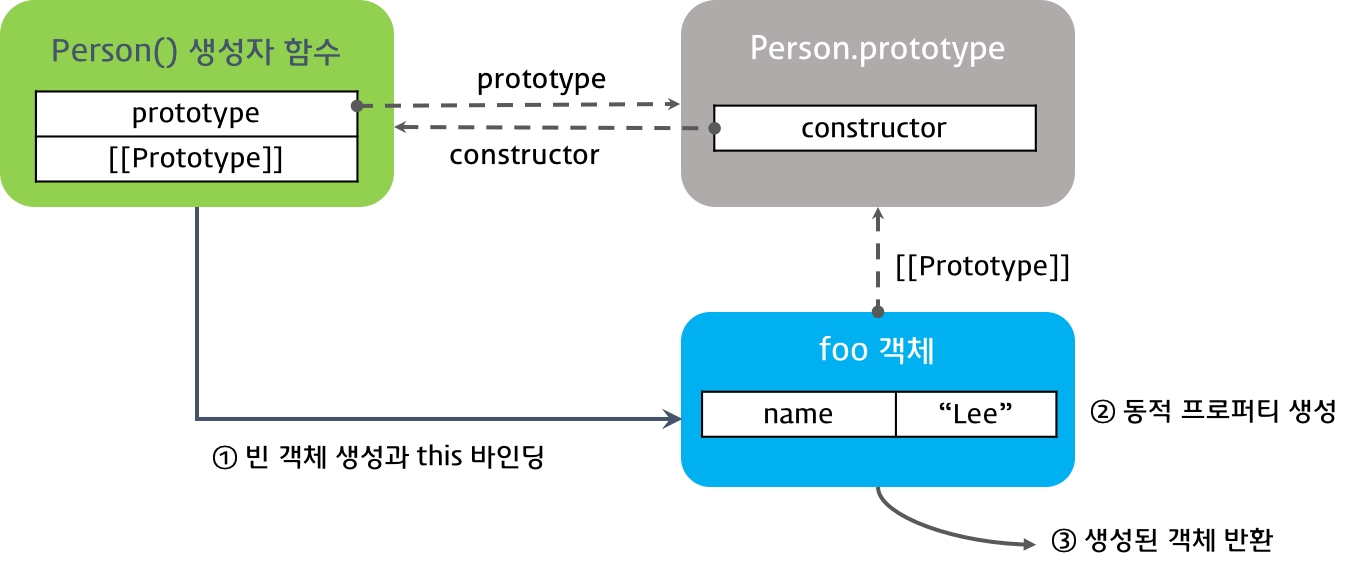
1. 빈 객체 생성 및 this 바인딩
빈 객체가 생성되고, 생성자 함수 내부의 this는 이 빈 객체를 가리킨다.
객체의
__proto__는 자신의 프로토타입 객체로 생성자 함수의 prototype object를 가리킨다. 이 객체는 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티가 가리키고 있다.
2. this를 통한 프로퍼티 생성
빈 객체에 동적으로 프로퍼티나 메서드를 생성한다. 이 때, this는 새로 생성된 객체를 가리키므로, this를 통해 생성한 프로퍼티와 메서드는 새로 생성된 객체에 추가된다.
3. 생성된 객체 반환
반환문이 없는 경우, this에 바인딩된 새로 생성한 객체가 반환된다. 명시적으로 this를 반환한 것과 같은 결과이다.
반환문이 this가 아닌 다른 객체를 명시적으로 반환한다면, this가 아닌 해당 객체가 반환된다. 해당 함수는 생성자 함수로서의 역할을 수행하지 못한다.
객체 리터럴 방식과 생성자 함수 방식의 차이
생성된 객체의 프로토타입 객체
객체 리터럴 방식 : Object.prototype
생성자 함수 방식 : 생성자 함수의 prototype이 가리키는 객체, 즉 Person.prototype
생성자 함수에 new를 붙이지 않고 호출할 경우
생성자 함수에 new를 붙이지 않고 호출할 경우, 일반 함수를 호출한 것이기에, this를 반환하지 않는다. 이 때 함수 내의 this는 전역 객체를 가리키게 된다.
이처럼 생성자 함수를 new 키워드 없이 호출하게 되면, new 키워드로 생성한 것과 다른 결과를 초래한다. 따라서 그러한 실수를 방지하고자 Scope-Safe Constructor로 생성자 함수를 만들게 된다. 이 패턴은 대부분의 라이브러리에서 광범위하게 사용된다.
arguments.callee는 함수 바디 내에서 현재 실행중인 함수의 이름이다. this가 현재 호출된 함수의 인스턴스가 아니라면, new 키워드 없이 호출된 함수이다. 따라서 new 키워드와 함께 생성자 함수를 호출하여, 새로운 객체에 this가 바인딩된 객체를 반환하도록 한다.
🌳 4. apply, call, bind 호출
기본적으로 this는 함수 호출 패턴에 따라 자바스크립트 엔진에 의해 this가 바인딩된다.
명시적으로 this를 특정 객체에 바인딩하려면, Function.prototype.apply, Function.prototype.call, Function.prototype.bind 메소드를 사용하면 된다.
func.apply(thisArg, [argsArray]) func.call(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
apply와 call은 this를 특정 객체에 바인딩할 뿐, 본질적인 기능은 함수 호출이다.
func.bind(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
bind 메서드는 인자로 받은 this가 바인드된 함수를 리턴한다. 따라서, 함수 호출을 따로 해주어야 한다.
명시적으로 this를 바인딩해줘야 하는 예시
(A)는 프로토타입 메서드 내부이므로 this가 해당 메서드를 호출한 인스턴스이지만, (B)는 일반함수이므로 (B)에서의 this는 전역 객체이다. 전역 객체에 relation은 없으므로, undefined를 반환하게 된다.
이렇게 콜백 함수의 this에 콜백함수를 호출한 함수의 this를 바인딩 시켜주어서 의도한대로 동작할 수 있도록 한다.
출처
Last updated